Arthritis, characterized by the swelling and tenderness of one or more joints, is a common ailment affecting millions globally. As individuals age, the predominant symptoms such as joint pain and stiffness often intensify. The condition can manifest in various forms, but osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis are the most prevalent.
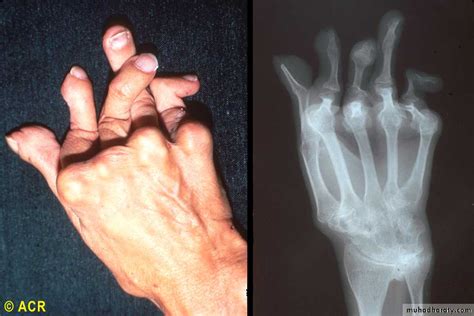
Arthritis isn’t merely a joint concern. Rheumatoid arthritis, a chronic inflammatory disorder, can affect more than just your joints. For some, this condition may harm various body systems, including the skin, eyes, lungs, heart, and blood vessels. As RA progresses, it leads to inflammation causing pain in joints like wrists, elbows, shoulders, ankles, knees, and even the C1-C2 vertebral regions.
On the other hand, osteoarthritis — the most prevalent form of arthritis — occurs when the protective cartilage cushioning bone ends deteriorates over time. This type of arthritis can affect any joint but is most common in the hands, knees, hips, and spine.
The term “arthritis” translates to “joint inflammation.” Inflammation is a body’s natural response to disease or injury. Alongside arthritis, other rheumatic diseases result in pain, swelling, and restricted movement, impacting joints and the connective tissues around the body. In the U.S. alone, millions suffer from some form of arthritis. These conditions center around joint inflammation, which is where two or more bones converge. Astoundingly, there are over 100 distinct arthritis-related diseases.
While arthritis in itself isn’t fatal, research indicates that complications from severe cases can reduce lifespan by six to seven years. However, there are numerous strategies to mitigate the risk of these complications.
In conclusion, arthritis, a broad term encompassing over 100 diseases, mainly leads to joint inflammation. Despite its non-fatal nature, severe cases can lead to complications that might affect one’s lifespan. Recognizing symptoms early and seeking appropriate treatment can help manage and possibly prevent these complications.


