Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune and inflammatory disease, characterized by the immune system mistakenly attacking healthy cells in the body. This results in painful swelling, primarily affecting multiple joints simultaneously, such as those in the hands, wrists, and knees. RA can significantly impact daily life, necessitating a comprehensive understanding of its symptoms, diagnosis, and management.
Early Signs and Diagnosis of Rheumatoid Arthritis
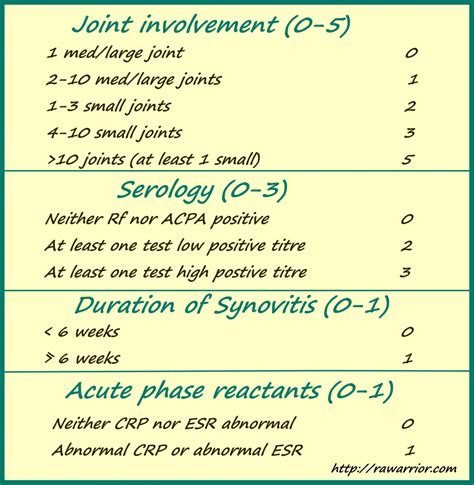
Early symptoms of RA include joint pain, stiffness, and swelling lasting more than six weeks, often affecting 3-4 different joints. Morning stiffness lasting over 30 minutes and symmetrical symptoms on both sides of the body are also common indicators. The diagnosis often involves a set of criteria, including the assessment of joint involvement and serology tests. According to the ACR/EULAR 2010 Rheumatoid Arthritis Classification Criteria, joint involvement is scored based on the number of small and large joints affected, while serology tests measure inflammation markers.
The Rheumatoid Arthritis Severity Scale (RASS)
The Rheumatoid Arthritis Severity Scale (RASS) aids doctors in determining disease activity, functional impairment, and physical damage caused by RA. This tool is vital for tailoring treatment plans to individual patient needs.
Managing Rheumatoid Arthritis
Management of RA typically involves Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs (DMARDs), with treatment initiated upon early diagnosis. Lifestyle adjustments, such as applying cold compresses to inflamed joints, using heat pads, and adopting suitable sleeping positions, can also alleviate symptoms. For instance, Rheumatoid Arthritis Sleep Positions can be crucial for better rest and reduced joint stress.
Genetic Factors and Innovative Detection Methods
Recent studies have explored genetic differences in RA patients, focusing on the role of Vitamin D and specific receptor genes like VDR FokI and TaqI polymorphisms. Additionally, novel detection methods using peptide-coated bacteriorhodopsin are being developed, highlighting advancements in RA research. For more on this, see the study at MDPI Biosensors.
Prevention and Future Directions
The idea of preventing RA in individuals with early arthralgia (joint pain) is gaining traction. While still in the research phase, this approach could transform RA management and outcomes.
For more comprehensive information on rheumatoid arthritis, its symptoms, diagnosis criteria, and management strategies, visit the CDC’s Rheumatoid Arthritis page and other resources linked throughout this article.