Arthritis is characterized by the inflammation or swelling of one or more joints, causing symptoms like joint pain and stiffness. With time, and especially with advancing age, these symptoms can intensify. Remarkably, arthritis isn’t just a single disease – it represents over 100 different conditions affecting joints, surrounding tissues, and other connective tissues. The type of arthritis one has determines its specific symptoms, intensity, and treatment approach.
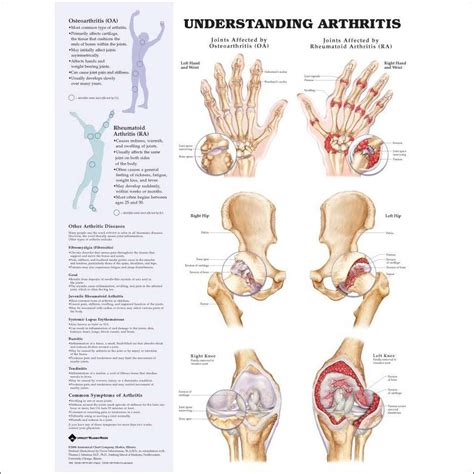
Osteoarthritis (OA): As the most prevalent form of arthritis globally, OA often develops in individuals in their mid-40s or later. The likelihood of encountering this type increases for women and those with a family history of OA. OA arises from the wear and tear of joint cartilage, leading to bones rubbing against each other. This results in pain, swelling, and reduced joint motion.
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA): RA is an autoimmune disorder where the body’s immune system attacks the joint’s lining. Over time, this can damage both cartilage and bone inside the joint. Pain, swelling, and joint deformity are common symptoms.
Psoriatic Arthritis (PsA): Tied to the skin condition psoriasis, PsA affects both skin and joints. It can develop at any age but commonly starts between the ages of 30 and 50. Symptoms range from skin rashes to joint pain.
Gout: A painful form of arthritis caused by excess uric acid forming crystals in the joints. These crystals cause sharp pain and swelling, often in the big toe.
Fibromyalgia: A disorder characterized by widespread muscle pain and fatigue. It’s often accompanied by sleep, memory, and mood issues.
Other types include Juvenile Arthritis, Lupus Arthritis, Reactive Arthritis, and Ankylosing Spondylitis. Each comes with its unique set of symptoms and challenges.
Understanding the specific type of arthritis is essential for targeted treatment and managing symptoms. It’s always recommended to consult with healthcare professionals for accurate diagnosis and guidance.
For a deeper dive into the types of arthritis and their implications, check out these resources: Healthline, Mayo Clinic, CDC, and WebMD.


